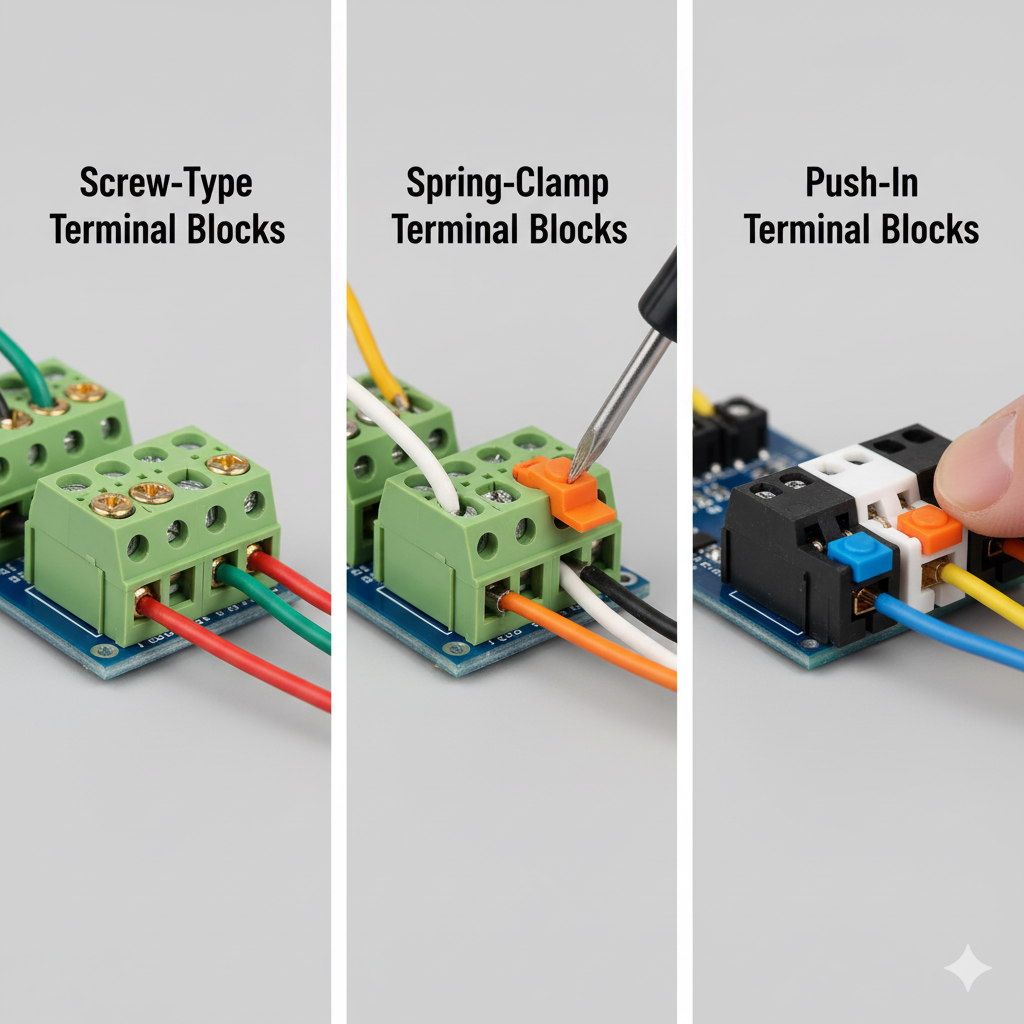
Reliable Wiring for Climate Control: Inside the HVAC Terminal Block Manufacturing Process
Heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems depend on accurate electrical control to regulate airflow, temperature, and pressure. At the heart of that reliability lies the HVAC terminal block—a small but essential component that distributes both power and control signals across compressors, fans, sensors, and control panels.
Without properly engineered terminal connections, HVAC systems face voltage drops, overheating, or maintenance failures that compromise operational stability.
Electrical and Mechanical Challenges in HVAC Systems
HVAC environments combine constant vibration, heat cycling, and humidity exposure, all of which put stress on connectors.
A qualified HVAC terminal block manufacturer must engineer against these stresses by focusing on:
-
Thermal endurance: materials sustaining >120 °C for compressor and heater control.
-
Vibration resistance: locking screws or spring clamps maintaining torque under oscillation.
-
Corrosion protection: nickel-plated brass contacts and anti-oxidation housings.
-
Compact installation: DIN-rail or panel-mounted designs fitting dense control boxes.
The goal is to achieve long-term current stability and eliminate maintenance downtime.
Engineering Design and Material Selection
| Component | Preferred Material | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | PA66 UL94 V-0 | Flame-retardant, UV and moisture-resistant |
| Contacts | Brass or copper alloy | High conductivity with minimal voltage loss |
| Screws | Zinc-plated steel | Consistent clamping under vibration |
| Mounting Base | Stainless steel / reinforced PC | Dimensional stability under heat load |
Designers apply finite-element stress analysis to predict deformation and ensure the mechanical life of 20 000 tightening cycles.
Each terminal is also tested under IEC 60947-7-1 dielectric and torque verification standards.
HVAC vs. General-Purpose Terminal Blocks
| Parameter | General Terminal Block | HVAC-Grade Terminal Block |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | −10 °C – 70 °C | −40 °C – 125 °C |
| Vibration Tolerance | Standard | Anti-vibration screw / spring cage |
| Humidity Resistance | Indoor only | Anti-oxidation, sealed housing |
| Current Rating | 10 – 20 A | 25 – 60 A continuous |
| Maintenance Interval | Frequent | Extended, torque-stable |
HVAC-specific models integrate heat-dissipating geometries and tight creepage distances to prevent dielectric failure inside compressor cabinets.
Manufacturing Standards and Process Control
Modern factories combine automated molding, robotic assembly, and digital inspection to guarantee repeatability:
-
High-pressure injection molding – ensures uniform wall thickness for insulation.
-
CNC screw insertion – maintains torque accuracy to ±0.02 Nm.
-
Thermal cycling test (−40 °C to 125 °C) – validates resistance to seasonal expansion.
-
Optical contact inspection – confirms alignment and seating precision.
Each batch receives a traceable lot number and passes 100% dielectric and pull-force testing, aligning with ISO 9001 and RoHS directives.
Application Scenarios Across HVAC Systems
| Application Area | Electrical Function | Recommended Type |
|---|---|---|
| Air-handling units (AHU) | Fan and motor wiring | Screw clamp, 30 A |
| Chillers and heat pumps | Compressor control | High-temperature spring clamp |
| Building automation panels | Sensor and signal circuits | Compact feed-through terminals |
| Industrial ventilation | Power distribution | Modular barrier terminal blocks |
| HVAC rooftops / outdoor units | Weather exposure | Sealed PA66 UV-resistant design |
Terminal blocks in HVAC systems must handle both high current and low-voltage control, often within the same enclosure—demanding hybrid electrical insulation strategies.
Selection Guidance for System Integrators
To optimize reliability and reduce maintenance overhead:
-
Choose UL94 V-0 housings for flame protection near heating coils.
-
Prefer spring-clamp models for vibration-intensive fans or compressors.
-
Maintain minimum 10 mm air gap between power and control circuits.
-
Use color-coded terminals for quick phase and sensor identification.
-
Request OEM-specific labeling or pre-assembled rail kits for faster field deployment.
An experienced supplier provides not just parts, but engineering documentation, test data, and customization options for seamless integration.
Advanced Questions from HVAC Engineers
Q1: How do HVAC terminal blocks prevent screw loosening from vibration?
A: By using serrated washers, captive screws, or spring cages maintaining elastic tension.
Q2: Are these components suitable for outdoor rooftop units?
A: Yes — provided they feature UV-stabilized PA66 and conformal sealing (IP ≥ 54).
Q3: What certifications should manufacturers provide?
A: UL1059, IEC 60947-7-1, CE, and RoHS compliance for export readiness.
Q4: How do high-temperature materials improve lifespan?
A: They prevent thermal creep and oxidation, keeping torque and conductivity stable beyond 10 years of cyclic load.
Empowering Climate Control Reliability Through Precision Engineering
As HVAC systems evolve toward smart, energy-efficient control, electrical reliability remains the foundation of performance.
Well-designed terminal blocks enable consistent connectivity under thermal, mechanical, and environmental stress — a silent but vital assurance of operational safety.
Zhongbo, as a dedicated HVAC terminal block manufacturer, combines automated precision molding, UL-certified materials, and OEM customization to support global air-conditioning and ventilation brands.
For engineering consultation or partnership opportunities, visit our homepage or contact us.